Researchers from Checkpoint have identified that a dubbed malware Gooligan has infected more than 1.3 million Android users globally.
Android targeted malware campaign infects devices and steals authentication tokens which is then used to access data from Google apps such as Google play, Gmail, google photos google docs, google drive and many others. The malware is a new variant of Gooligan, which was discovered by Checkpoint last year with a primary intension to boost advertising revenue from infected apps.
Affected versions: Android 4 Jelly Bean, Android 4 KitKat and Android 5 Lollipop. These versions covers approx. 74% of all the Android users around the world. The percentage distribution of users infected by this malware as follows.
- 57% of users are from Asia
- 19% of users are from Americas
- 15% of users are from Africa
- 9% of the users are from Europe
Checking your google account for breach:
Checkpoint has provided a website where you can provide your user email and validate if it was breached. https://gooligan.checkpoint.com
If your account is compromised please follow the following steps:
- Change the password of your google accounts immediately and refrain from using your device till next step if completed.
- Rebuild or perform clean installation of Android operations system which is also called as flashing. It can be advanced hence please contact your local technician whichever is easier.
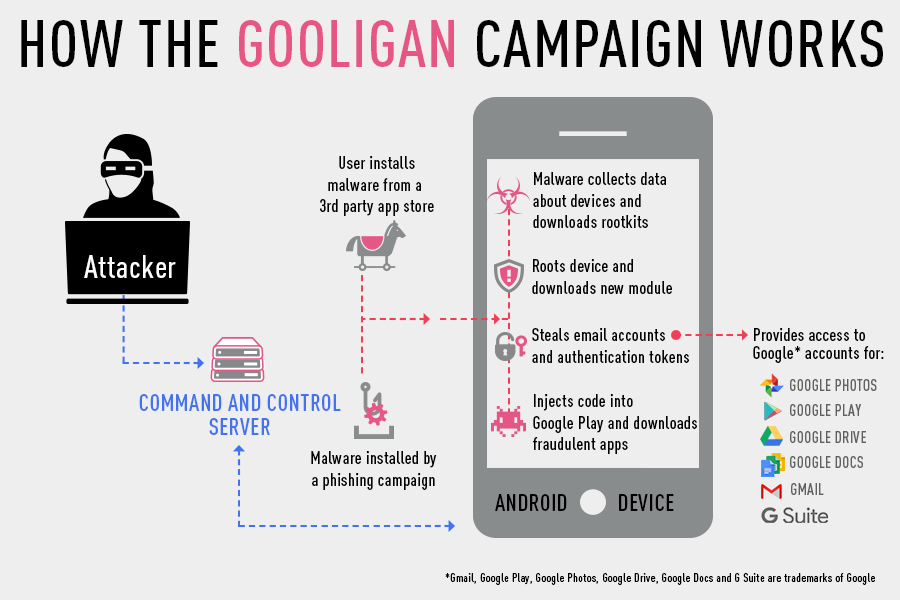
How does this malware Gooligan works?
When a user downloads gooligan malware infected apps from the app store, either by a phishing text, scam, fb post or any other means and installs, the android device gets infected. Once the infected app is installed, the app sends out the details of the device to the Command & Control (C&C) server. Upon contacting C&C, the app downloads a rootkit from the server and injects exploits to the vulnerable device. [(VROOT (CVE-2013-6282) and Towelroot (CVE-2014-3153)]. If the exploitation if possible then the attacker will have full control of the device and can execute any commands remotely.
Once the Android device is infected, the malware tries to contact C&C and then tries to install new malicious module on the device. The Gooligan malware later injects code into google play / other services to replicate the user behavior similar to malware Hummingbad to boost the advertising revenue.
Pic Ref : Checkpoint Blog
The malware app earn money in two ways. Every app installed results in a payment to the attacker, while apps also earn revenue from ad services that pay to distribute ads through installed apps. The malware also forces infected devices to leave positive review and a higher rating on Google Play.
Google Authentication Tokens:
In simple words, this is a way to access google accounts and services which is issued by Google upon login.
When a Google authorization token is stolen by a hacker, they can use this token to access all the Google services related to the user (includes Google Play, Gmail, Google Docs, Google Drive, Google Photos and may other google services) .While Google implemented multiple mechanisms, like two-factor-authentication, to prevent hackers from compromising Google accounts, a stolen authorization token bypasses this mechanism and allows hackers the desired access as the user is perceived as already logged in. ( Reference : Checkpoint )
Google is still in denial that there is no evidence that the access might have taken place where a Checkpoint has shown to the world about its latest research with valid data.
Ref : Checkpoint