A mobile app development company has been identified as the perpetrator of distributing malicious applications globally and hacking the Android phones of users on whose devices these apps are installed. The apps grant complete access to the Android devices of the users and the attackers can gain total control over these devices.
These malware apps have been discovered by the researchers at FireEye Labs. The company responsible and distribution of the malicious adware is NGE Mobi/Xinyinhe. The company operates from China and Singapore and claims to have a valuation of over US$100 million.
The technique used by the malware is unique and it efficiently hides its activities. The malware is able to install services at the system level and can even modify the recovery script that is executed when the system is booted. It can also deceive the device owners to enable automatic installation of apps. The malware uses illegal versions of over 300 commonly used Android applications that include Amazon, Clean Master, Memory Booster, Flashlight and YTD Video Downloader.
Since the adware is able to take complete control of the devices of the users, the company guarantees that the apps it is promoting will be downloaded. The company is also able to generate substantial ad revenue by installing the adware on the hacked devices.
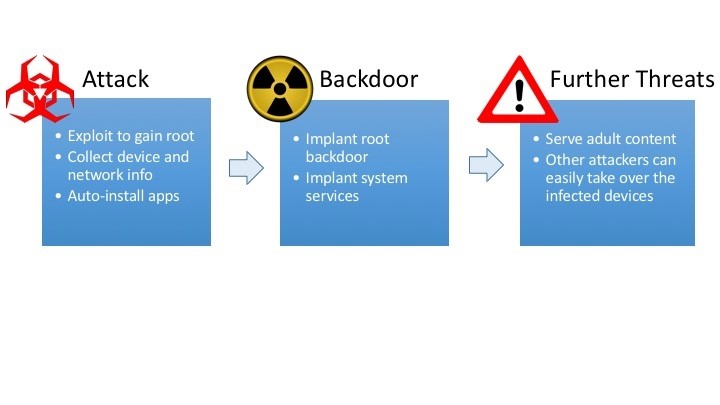
Attack scenario:
Attack – It involves exploiting the system and gain access to root. Collecting network and device information and auto installing apps.
Backdoor – It implants root backdoor and other system services.
Exploitation – The adware displays adult content and grants access to other attackers who can then take over complete control of the infected devices.
(Image source: www.fireeye.com)
The attack has infected devices in 26 countries across 4 continents and has affected 308 phone models. 20 versions of Android starting from 2.3.4 build to 5.1.1 have been infected. From August this year, the attack is being monitored by FireEye and it has been observed that the attack continues to grow.
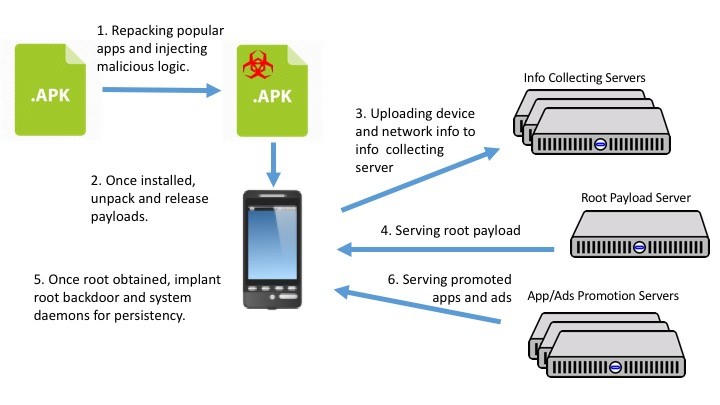
Modus operandi of the malware:
- The attackers inject malicious codes in popular apps and repackage them which are then disseminated to the users through various modes. Victims are unable to differentiate between these apps and the original applications and are tricked into downloading the malicious app.
- Once the users install the app, the malicious payload is unpacked and released.
- The malware then transmits the details of the device to the collecting server.
- The server then transmits root payload.
- The received payload installs root backdoor.
- Through the root backdoor, the server then transfers adware and other apps to the victim’s device
(Image source: www.fireeye.com)
When the malware transmits devices’ information to the servers, below domains are iterated till the time the connection is established and the data is posted.
Aedxdrcb.com
Hdyfhpoi.com
Syllyq1n.com
Wksnkys7.com
The device info is encoded and encrypted and transmitted by the adware to the server using AES/CBC/NoPadding and Base64. It includes basic details of the device such as the IMEI number and other device details.
It them downloads an APK file from the below link which is then installed on the device: http://down.onowcdn.com/onekeysdk/tr_new/rt_0907_129.apk
Once installed, the APK roots the device of the victim and loads root master. The app then installs few native executable and a shell script. Through this method, the app is able to completely control the device and an attacker can then exploit the root backdoor to gain an access to the Android device.
Security Measures:
The researchers have suggested that the users must refrain from clicking on suspicious links and must install apps only from the authorized application store. Updating the OS version might also temporarily give a protection from the malware till the time the attackers also update the malware to take control of the new OS versions. The users must take appropriate steps and may install apps that will protect their devices.